Which of the following food contaminations would be suspected? This question delves into the intricate world of food safety, exploring the various types of contaminants that can jeopardize the quality and safety of our food supply.
From microbial intruders to chemical trespassers and physical hazards, this article unravels the complexities of food contamination, shedding light on the sources, detection methods, and preventive measures that safeguard our sustenance.
Microbial Contaminants
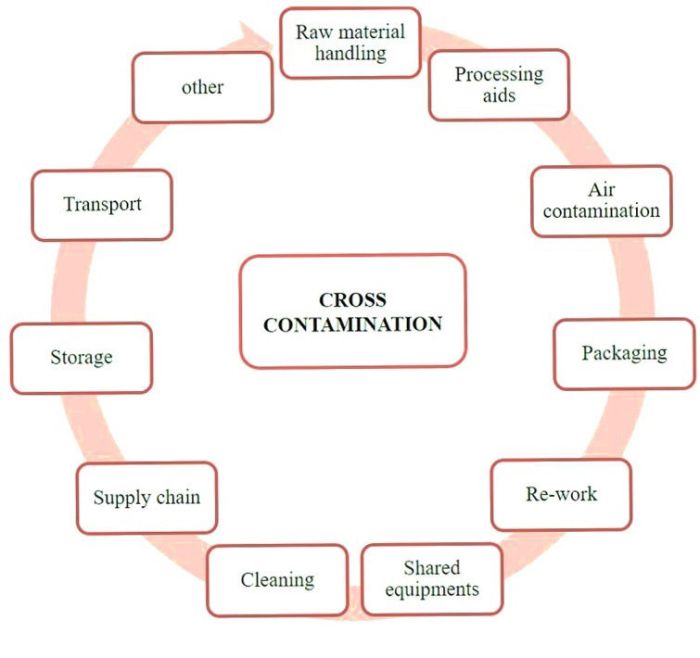
Microbial contaminants are microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, that can contaminate food and cause foodborne illnesses. These contaminants can enter food through various sources, including animals, soil, water, and food handlers.
Types of Microbial Contaminants
- Bacteria: Salmonella, E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes
- Viruses: Norovirus, Hepatitis A virus
- Fungi: Aspergillus, Candida
- Parasites: Toxoplasma gondii, Trichinella spiralis
Conditions Favoring Microbial Growth
Microbial growth in food is influenced by several factors, including temperature, pH, water activity, and nutrient availability. Optimal conditions for microbial growth typically include warm temperatures, neutral pH, high water activity, and the presence of nutrients.
Chemical Contaminants
Chemical contaminants are non-microbial substances that can enter the food supply from various sources, including agricultural practices, industrial processes, and environmental pollution.
Types of Chemical Contaminants
- Pesticides: Herbicides, insecticides, fungicides
- Heavy metals: Lead, mercury, cadmium
- Industrial chemicals: Dioxins, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
- Natural toxins: Mycotoxins (produced by fungi), marine biotoxins
Routes of Entry into Food
Chemical contaminants can enter food through various routes, including:
- Agricultural practices: Pesticide application, animal feed
- Industrial processes: Food processing, packaging materials
- Environmental pollution: Air and water contamination
Physical Contaminants
Physical contaminants are foreign objects that can be found in food, such as hair, glass, metal fragments, and stones. These contaminants can enter food during harvesting, processing, packaging, or transportation.
Types of Physical Contaminants
- Hair and other human materials
- Glass and metal fragments
- Stones and other natural materials
- Plastic and other packaging materials
Detection and Removal
Physical contaminants are typically detected through visual inspection, metal detectors, and X-ray machines. Removal methods include sieving, filtration, and manual sorting.
Foodborne Illnesses

| Foodborne Illness | Symptoms | Contaminant Type |
|---|---|---|
| Salmonella | Diarrhea, vomiting, fever | Bacteria |
| Norovirus | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | Virus |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Fever, muscle aches, nausea | Bacteria |
| Ciguatera poisoning | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, neurological symptoms | Natural toxin |
Foodborne illnesses can range from mild to severe and can even be fatal in some cases. It is essential to practice proper food safety measures to prevent food contamination and reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Food Safety Regulations

Food safety regulations are essential in preventing food contamination and ensuring the safety of the food supply. These regulations are established by government agencies and cover various aspects of food production, processing, and distribution.
Impact of Food Safety Regulations
- Reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses
- Protect consumer health
- Promote fair trade practices
- Facilitate international food trade
Challenges and Opportunities, Which of the following food contaminations would be suspected
Implementing and enforcing food safety regulations can be challenging due to factors such as:
- Global food supply chains
- Emerging foodborne pathogens
- Consumer demand for convenience foods
However, food safety regulations also present opportunities for:
- Innovation in food safety technologies
- Collaboration between industry and government
- Education and outreach programs
FAQ Guide: Which Of The Following Food Contaminations Would Be Suspected
What are the most common types of foodborne illnesses?
Foodborne illnesses can be caused by a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
How can I prevent foodborne illnesses?
Proper food handling and preparation practices, such as thorough cooking, avoiding cross-contamination, and maintaining proper storage temperatures, are crucial in preventing foodborne illnesses.
What are the symptoms of foodborne illnesses?
Symptoms of foodborne illnesses can vary depending on the specific contaminant, but may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever.
