Two plane mirrors intersect at right angles. A laser beam, a beacon of light, embarks on an intriguing journey as it encounters these mirrors, inviting us to unravel the captivating interplay of reflection and geometry.
The laws of optics govern the laser beam’s interactions with the mirrors, dictating its path and revealing the intricate dance of angles and reflections. As the beam traverses this optical labyrinth, it illuminates the fundamental principles that shape the behavior of light.
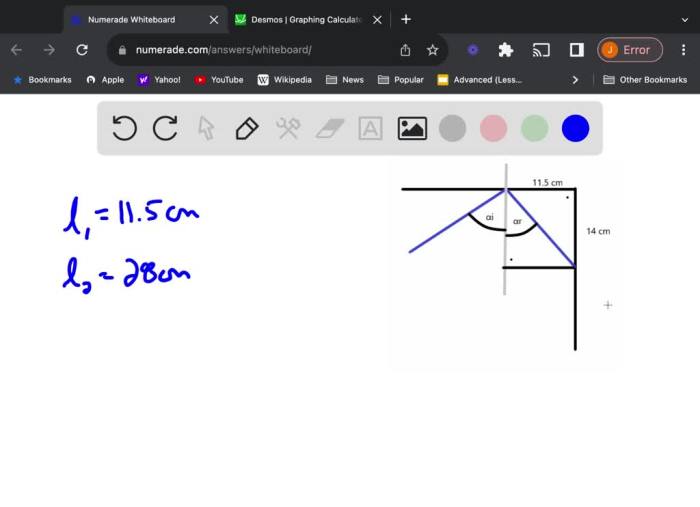
Two Plane Mirrors Intersect at Right Angles: Two Plane Mirrors Intersect At Right Angles. A Laser Beam
Two plane mirrors intersect at right angles, forming a corner. A laser beam is directed towards one of the mirrors.
Reflection of Laser Beam from One Mirror
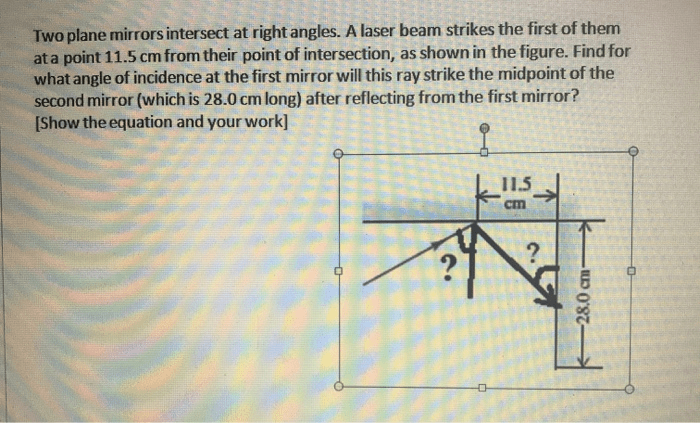
The laser beam strikes the first mirror at an angle of incidence θ1. According to the laws of reflection, the angle of reflection θ2 is equal to the angle of incidence, and the reflected beam lies in the same plane as the incident beam and the normal to the mirror.
Reflection of Laser Beam from Intersecting Mirrors
The reflected beam from the first mirror strikes the second mirror at an angle of incidence θ3. Again, the angle of reflection θ4 is equal to the angle of incidence, and the reflected beam lies in the same plane as the incident beam and the normal to the mirror.
Number of Reflections
The laser beam continues to reflect back and forth between the two mirrors, undergoing multiple reflections. The number of reflections depends on the angle of incidence and the distance between the mirrors.
Applications, Two plane mirrors intersect at right angles. a laser beam
This optical setup has potential applications in laser systems, optical communication, and other fields.
- Laser systems: The multiple reflections can be used to increase the intensity of the laser beam or to create specific beam patterns.
- Optical communication: The reflections can be used to guide light signals through optical fibers or to create optical switches.
Quick FAQs
What is the angle of reflection when a laser beam strikes a mirror?
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, both measured from the normal to the mirror’s surface.
How many times will a laser beam reflect between two intersecting mirrors?
The number of reflections depends on the angle of incidence and the geometry of the mirrors. In the case of two mirrors intersecting at right angles, the beam will reflect indefinitely.
What are some applications of multiple reflections between mirrors?
Multiple reflections can be used in laser systems to achieve specific beam patterns, in optical communication to transmit signals over long distances, and in optical sensors to detect objects.
