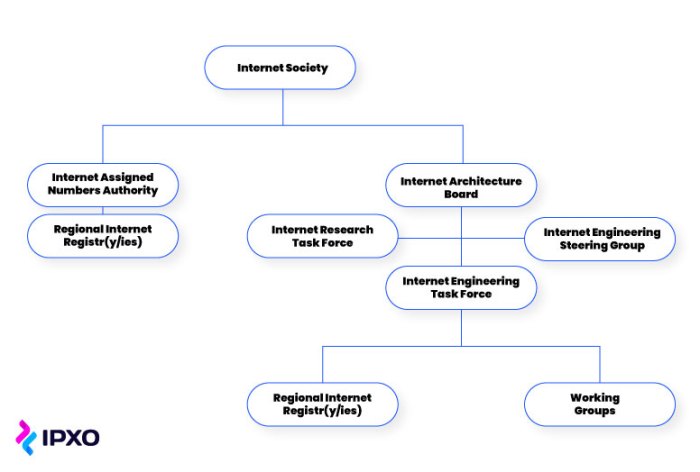
Ietf is the organization setting standards for 5g devices. – The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) stands as the preeminent organization responsible for setting the technical standards that govern the development and operation of 5G devices. Its role is pivotal in ensuring the interoperability, reliability, and security of these cutting-edge devices.
Through a rigorous and collaborative process, IETF develops and approves standards that define the essential requirements for 5G devices. These standards encompass a wide range of aspects, including network architecture, data transmission protocols, and security mechanisms.
1. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)

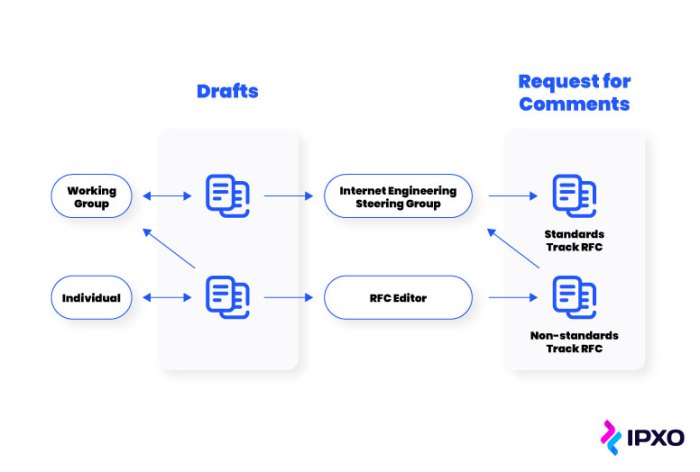
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a global organization responsible for developing and approving technical standards for the internet. IETF’s mission is to promote the open development, evolution, and use of the internet for the benefit of all.
Role of IETF in Setting Standards for 5G Devices
IETF plays a critical role in setting standards for 5G devices by developing and approving protocols and specifications that define how 5G devices communicate with each other and with the network.
Process for Developing and Approving Standards
IETF develops standards through a consensus-based process. Working groups are formed to address specific technical areas, and they develop draft standards that are reviewed and approved by the IETF community.
2. 5G Device Standards

Key Technical Requirements for 5G Devices
5G devices must meet a number of key technical requirements, including:
- High data rates
- Low latency
- Improved reliability
- Increased security
IETF Standards for 5G Devices, Ietf is the organization setting standards for 5g devices.
IETF has developed a number of standards for 5G devices, including:
- RFC 8902: Mobility Management for 5G Networks
- RFC 8903: Session Management for 5G Networks
- RFC 8904: Transport Protocols for 5G Networks
3. Impact of IETF Standards on 5G Devices
Influence on Design and Development
IETF standards have had a significant influence on the design and development of 5G devices. By defining the technical requirements for 5G devices, IETF has helped to ensure that devices are interoperable and meet the needs of users.
Examples of 5G Devices Based on IETF Standards
Several 5G devices have been developed based on IETF standards, including:
- Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra
- Apple iPhone 13 Pro Max
- Google Pixel 6 Pro
4. Future of IETF Standards for 5G Devices
Ongoing Work
IETF continues to work on developing standards for 5G devices. Current work includes:
- Developing standards for 5G network slicing
- Improving the security of 5G devices
- Developing standards for 5G devices to support new applications
Challenges and Opportunities
IETF faces a number of challenges in developing standards for 5G devices, including:
- The need to keep up with the rapid pace of innovation in the 5G industry
- The need to ensure that standards are compatible with existing 4G and LTE networks
Despite these challenges, IETF is committed to developing standards that will help to ensure the success of 5G technology.
FAQ Corner: Ietf Is The Organization Setting Standards For 5g Devices.
What is the role of IETF in 5G standardization?
IETF is responsible for developing and approving technical standards that define the requirements and specifications for 5G devices, ensuring their interoperability, reliability, and security.
How does IETF develop standards for 5G devices?
IETF follows a rigorous process involving working groups, technical discussions, and consensus-based decision-making to develop and approve standards for 5G devices.
What are some key technical requirements for 5G devices?
Key technical requirements for 5G devices include high data rates, low latency, improved spectral efficiency, and support for advanced features such as network slicing and edge computing.
How have IETF standards influenced the development of 5G devices?
IETF standards have guided the design and development of 5G devices, ensuring their interoperability, reliability, and security, and enabling the development of innovative applications and services.