Atp the free energy carrier worksheet answer key – ATP: The Free Energy Carrier Worksheet Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of the critical role of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in cellular processes. This worksheet delves into the structure, function, and applications of ATP, empowering students with a deeper understanding of this essential energy molecule.
ATP, the universal energy currency of cells, plays a pivotal role in various cellular activities, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and DNA synthesis. Understanding the intricacies of ATP metabolism is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of cellular biology.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP): The Free Energy Carrier: Atp The Free Energy Carrier Worksheet Answer Key
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the universal energy currency of cells. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, providing the energy required for essential functions.
ATP consists of an adenine base, a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups. The high-energy bonds between the phosphate groups allow ATP to release energy when hydrolyzed, making it an ideal energy carrier.
Structure and Components of ATP, Atp the free energy carrier worksheet answer key
ATP is composed of three main components:
- Adenine:A nitrogenous base that forms the core of the ATP molecule.
- Ribose:A pentose sugar that provides the backbone for the molecule.
- Phosphate groups:Three phosphate groups attached to the ribose sugar. The high-energy bonds between these phosphate groups are responsible for ATP’s energy-carrying capacity.
Energy Transfer and Hydrolysis
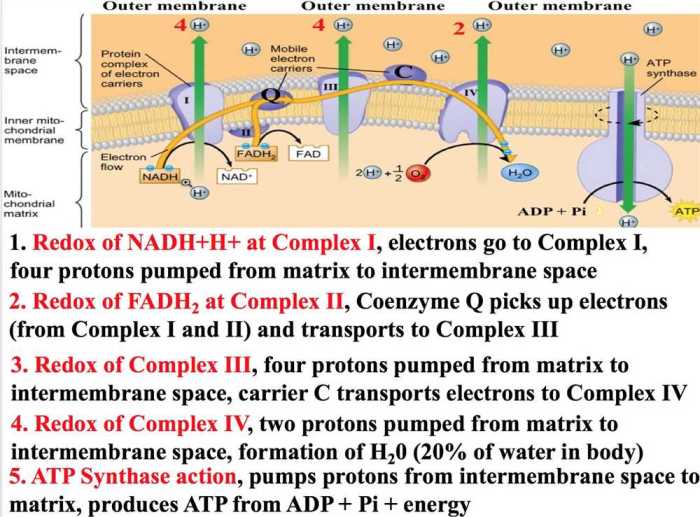
ATP releases energy through hydrolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks the high-energy bonds between the phosphate groups.
The hydrolysis of ATP is catalyzed by enzymes called ATPases. ATPases facilitate the transfer of the terminal phosphate group to other molecules, releasing energy in the process.
Regulation of ATP Levels
Cellular activities influence ATP levels through the processes of ATP synthesis and breakdown:
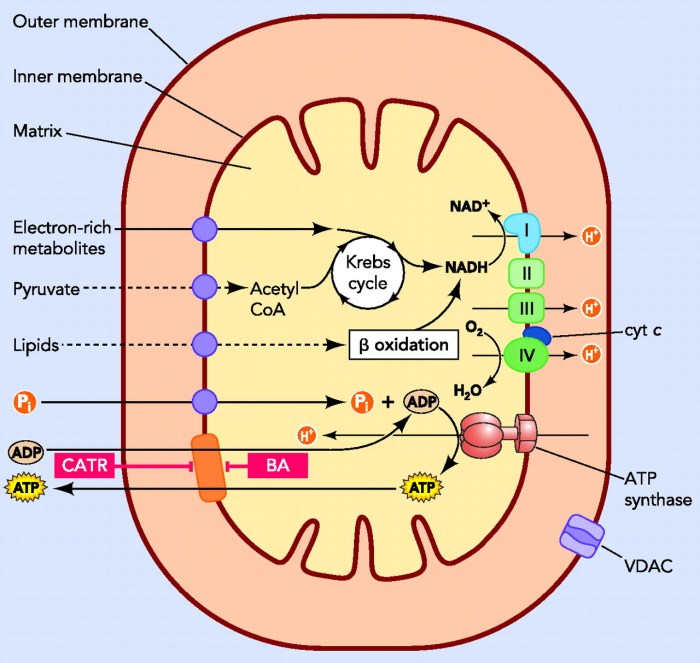
- ATP synthesis:ATP is synthesized primarily through oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria and glycolysis in the cytoplasm.
- ATP breakdown:ATP is broken down through hydrolysis, catalyzed by ATPases, to provide energy for cellular processes.
ATP in Cellular Processes
ATP is essential for a wide range of cellular processes, including:
- Muscle contraction:ATP provides the energy for muscle fibers to contract.
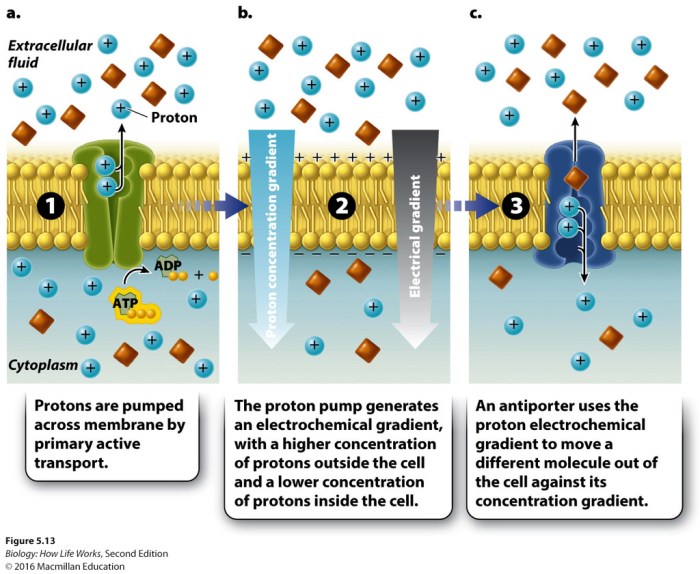
- Nerve impulse transmission:ATP powers the sodium-potassium pump, which maintains the electrochemical gradient necessary for nerve impulses.
- DNA synthesis:ATP provides the energy for DNA polymerase to add nucleotides during DNA replication.
Applications in Biotechnology
ATP has numerous applications in biotechnology:
- ATP-based biosensors:ATP levels can be measured using ATP-based biosensors, providing insights into cellular metabolism and disease states.
- ATP assays:ATP assays are used to determine the concentration of ATP in cells or tissues, which can be indicative of cellular health and viability.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary function of ATP in cells?
ATP serves as the universal energy carrier in cells, providing the necessary energy for various cellular processes.
How does ATP release energy?
ATP releases energy through hydrolysis, a process that breaks the bond between the terminal phosphate group and the rest of the molecule.
What are the key components of ATP?
ATP consists of three main components: adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups.