Embark on a scientific journey with our comprehensive Conduction Convection or Radiation Worksheet Answer Key. This meticulously crafted resource delves into the fundamental principles of heat transfer, providing a thorough understanding of the mechanisms and factors influencing each mode.
Through engaging explanations, illustrative examples, and insightful discussions, this guide empowers learners to grasp the intricacies of conduction, convection, and radiation. Prepare to unlock the secrets of heat transfer and enhance your scientific knowledge with this indispensable tool.
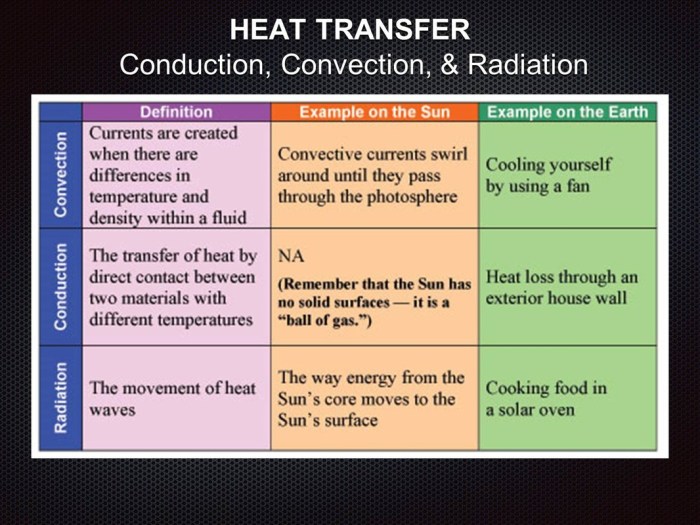
Conduction, Convection, and Radiation

Heat transfer is the movement of thermal energy from one object to another. There are three main modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects. When two objects with different temperatures touch, heat flows from the hotter object to the cooler object until they reach the same temperature. The rate of heat transfer by conduction depends on the temperature difference between the objects, the area of contact between the objects, and the material of the objects.
- Examples of conduction:A metal spoon in a hot cup of coffee, a cold hand on a warm steering wheel, a heat sink on a computer processor.
- Factors affecting conduction:Temperature difference, contact area, material conductivity.
Convection, Conduction convection or radiation worksheet answer key
Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of fluids. When a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises. This creates a current of fluid that carries heat away from the heat source. Convection currents can occur in liquids, gases, and plasmas.
- Examples of convection:A boiling pot of water, a convection oven, the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Factors affecting convection:Temperature difference, fluid density, fluid viscosity, gravity.
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, so radiation can occur even when there is no contact between objects. The rate of heat transfer by radiation depends on the temperature of the objects, the emissivity of the objects, and the distance between the objects.
- Examples of radiation:The sun’s heat reaching the Earth, a fire radiating heat, a microwave oven.
- Factors affecting radiation:Temperature, emissivity, distance.
Comparison of Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
| Mode of Heat Transfer | Definition | Mechanism | Examples | Factors Affecting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Heat transfer through direct contact | Heat flows from hotter to cooler object | Metal spoon in hot coffee | Temperature difference, contact area, material conductivity |
| Convection | Heat transfer by fluid movement | Heated fluid rises, creating currents | Boiling water | Temperature difference, fluid density, fluid viscosity, gravity |
| Radiation | Heat transfer by electromagnetic waves | Waves travel through vacuum | Sun’s heat reaching Earth | Temperature, emissivity, distance |
Clarifying Questions: Conduction Convection Or Radiation Worksheet Answer Key
What is the difference between conduction, convection, and radiation?
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects, convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids, and radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
Which mode of heat transfer is most efficient?
Radiation is the most efficient mode of heat transfer, as it does not require a medium to travel through.
What factors affect the rate of heat transfer?
The rate of heat transfer is affected by the temperature difference between the objects, the surface area of the objects, the distance between the objects, and the material properties of the objects.